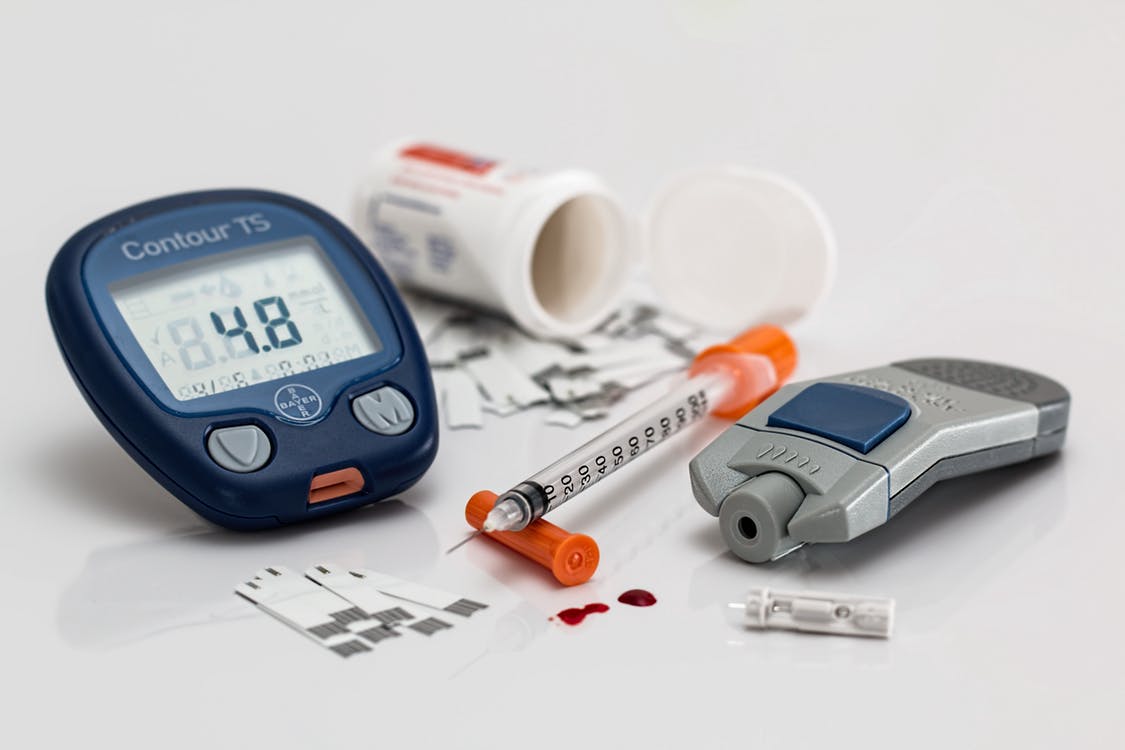
Be Amazingly Healthy: 5 Facts About In Vitro Diagnostics
04-06-2019 | Posted By: Admin | 2224 View(s)
Through the years, healthcare and medicine, overall, has become a significant aspect of people’s lives. As time goes by, a lot of devices and techniques are discovered, and one of those is the In Vitro Diagnostics.
As an integral part of healthcare, in vitro diagnostics (IVD) enables the healthcare professionals to screen, diagnose, treat, monitor, and manage the diseases. Learn more about IVD through the facts below.
What is In Vitro Diagnostics?
In Vitro Diagnostics (IVDs) are medical devices and accessories used to perform tests on samples, (e.g., blood, urine, and tissue that has been taken from the human body) to: help detect infection, diagnose a medical condition, and prevent diseases.
Devices can range from simple tests to sophisticated DNA technology including calibrators, reagents, control materials, software, kits, and related instruments.

One of the most critical segments in the global healthcare industry is the IVD. The marketplace is witnessing rapid growth fuelled by technological advancements, improved treatment monitoring, better diagnostic tools, and increased availability of over-the-counter tests.
IVDs add significant value to medical diagnoses and treatment processes, enhancing the well-being of the general public.
Is In Vitro Diagnostics Important?
To diagnose, monitoring, screening, and prognosis, in vitro diagnostic tests are essential at every step.
Beyond these purposes of diagnostic tests, it’s important to know that they do not treat patients or cure illnesses, but are an integral step toward both. They do not come into direct contact with the patient as they only need a sample from the patient to produce results.
The impact of these results on healthcare decisions is significant and vital, though it also relies on a medical professional’s accurate judgment and appropriate choice of treatment. In vitro diagnostic tests serve as a guide providing essential information on health and the care of it.
How Does It Work?
In Vitro Diagnostic (IVD) tests can be described merely as a subset of medical devices which is used for in vitro examination of specimens.
These specimens are derived from the human body to provide information for screening, diagnosis, or treatment monitoring purposes.
An IVD test may include reagents provided either in kit format or separately, as well as controls, and calibrators. In vitro testing may be performed on a variety of instruments ranging from small, handheld tests to complex laboratory instruments.
Moreover, a wide range of enzyme-linked immunoassays (EIAs), the most widely used IVD assays in clinical diagnostics, have been developed. Their deployment has contributed to considerable advances in healthcare.
Types of Enzyme Immunoassay (EIA)
Radioimmunoassay (RIA)
Radioimmunoassay is a sensitive, specific laboratory test that uses unlabeled and radiolabeled substances in an immunological reaction.
It is an in vitro assay with very high sensitivity which measures the presence of an antigen. Even in minute concentrations, any biological substance for which a specific antibody exists can be measured.
Counting Immunoassay (CIA)
Polystyrene beads are coated with many antibodies complementary to the target antigen in a counting immunoassay. While some beads remain unbound, the beads bind to multiple antigens and group together into a large mass during incubation.
Only the unbound beads are counted when the entire solution is passed through a cell counter. The amount of antigen is inversely proportional to the number of unbound beads.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA)
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) is a microplate-based technique for detecting and quantifying substances such as peptides, proteins, antibodies, and hormones.
An antigen must be immobilized on a solid surface and then complexed with an antibody that is linked to an enzyme in an ELISA.
Fluoroimmunoassay (FIA)
Fluoroimmunoassay offers an alternative signal generation and detection system to RIA with potentially greater sensitivity.
The antibodies are labelled with fluorescent probes in a fluoroimmunoassay. The antibody-antigen complexes are isolated, and the fluorescent intensity is measured after incubation with antigen.
Chemiluminescence Immunoassay (CLIA)
Chemiluminescence immunoassay (CLIA) is an assay that combines chemiluminescence technique with immunochemical reactions. It is a variation of the standard EIA which is a biochemical technique used in immunology.
Chemiluminescence immunoassay can also be used as diagnostic tools in medicine, as well as being in used in several other different industries for various applications.
Role of In Vitro Diagnostics in Healthcare
In Vitro Diagnostics (IVD), it has been estimated that IVD will play a role in around 70% of health care decisions and market estimates predict the IVD market will be close to 75 billion dollars in 2010.
The role of IVDs in health care decisions would only continue to grow as healthcare shifts away from a “one-size-fits-all” model.
Furthermore, developments in the scope and precision of some of these devices and technology have led to the evolution of the IVD field and with it, the role the FDA has played in regulating these devices.
Takeaway
IVDs are a crucial component of clinical care. They are becoming increasingly familiar, as the use of self-tests, such as for pregnancy tests and blood glucose monitoring for people with diabetes becomes more common.
It is crucial to know more about the primary and developing treatments and interventions regarding healthcare. It is only right to understand the things that you can do or avail to live a long life in a healthy body.


